White Paper on Heat Dissipation Technology for High-Power LEDs
White Paper on Heat Dissipation Technology for High-Power LEDs
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of LEDs technology, high-power LEDs have been widely used in lighting, display and industrial applications. However, since high-power LEDs generate a lot of heat during operation, heat dissipation becomes a key factor affecting their luminous efficacy, life and reliability. This white paper will explore the heat dissipation technology of high-power LEDs and analyze the advantages and disadvantages of different heat dissipation solutions.
2. Heat Dissipation Challenges of High-Power LEDs
2.1 Heat Source Analysis
Due to their high electro-optical conversion efficiency, a considerable amount of energy of high-power LEDs is still converted into heat. If the heat cannot be dissipated in time and effectively, it will cause the junction temperature to rise, affecting the luminous efficacy and shortening the life of LEDs.
2.2 Importance of Thermal Management
The thermal management of LEDs directly affects their reliability. Studies have shown that for every 10°C increase in LED junction temperature, its life will be reduced by about 50%. Therefore, an efficient heat dissipation solution is crucial for the stable operation of high-power LEDs.
3. High-power LED heat dissipation technology
3.1 Passive heat dissipation
3.1.1 Aluminum-based heat sink
Aluminum alloy has good thermal conductivity and is a common material for LED heat sinks. By optimizing the heat sink structure, the heat conduction and convection heat dissipation capabilities can be improved.
3.1.2 Heat pipe technology
Heat pipes use the phase change principle to quickly conduct heat, which can greatly improve the heat dissipation efficiency and are often used in high-power LED lighting systems.
3.1.3 Graphene heat sink
Graphene has extremely high thermal conductivity and can effectively and evenly distribute heat in LED modules to reduce local overheating problems.
3.2 Active heat dissipation
3.2.1 Air-cooled heat dissipation
The fan accelerates air flow and improves the convection heat dissipation effect, which is suitable for high-power LED devices.
3.2.2 Liquid-cooled heat dissipation
The liquid coolant is circulated to remove heat, which is often used in ultra-high-power LED applications such as stage lighting and car headlights.
3.2.3 Micro-thermoelectric cooling
Active cooling using the thermoelectric effect is more expensive but suitable for temperature-sensitive high-end LEDs.
4. Trends in advanced heat dissipation materials and technologies
4.1 Phase change materials (PCM)
Phase change materials can store and release a large amount of thermal energy and can be used for thermal management of LED lighting systems.
4.2 Nano-heat dissipation coatings
Nano-coatings can improve the radiation capacity of the heat dissipation surface of LEDs, thereby enhancing heat dissipation performance.
4.3 3D printed heat sinks
3D printing technology can manufacture heat sinks with complex structures to optimize heat flow paths and improve heat dissipation efficiency.
5. Conclusion and future prospects
The heat dissipation management of high-power LEDs is critical to their performance and life. Current heat dissipation solutions include passive heat dissipation and active heat dissipation, and the development of new materials and technologies is driving the continuous improvement of heat dissipation efficiency. In the future, with the development of nanotechnology, phase change materials and intelligent thermal management systems, the heat dissipation problem of high-power LEDs will be further optimized, providing support for more efficient and reliable LED solutions.
About Us
We focus on the research of LEDs lighting technology and heat dissipation solutions, providing customers with efficient and reliable product design and optimization solutions. If you want to know more, please contact us.
 Infrared LED Technology White Paper
Infrared LED Technology White Paper
 Industrial LED Selection Guide White Paper
Industrial LED Selection Guide White Paper
 LED Plant Spectrum White Paper
LED Plant Spectrum White Paper
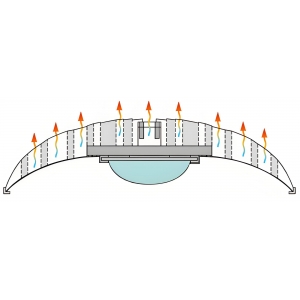 White Paper on High-Power LED Heat Dissipation (2025 Edition
White Paper on High-Power LED Heat Dissipation (2025 Edition
- PRODUCTS
- HIGH POWER WHITE
- HIGH POWER COLOR
- COLOR LEDs
- INFRARED LEDs
- UV LEDs
- MINI LEDs
- COB LEDs
- INTEGRATED MOULES
- MARKETS SERVED
- LIGHTING LEDs
- AUTOMOTIVE LEDs
- BIOMEDICAL LEDs
- DISPLAY LEDs
- CURING DISINFECTION LEDs
- PLANT LEDs
- INFRARED SECURITY LEDs
- VISION LEDs
CONTACT US
TEL:+86-0769-81305858
PH:+8613612789419
E-mail:sales@queendomlamp.com